Normal Calcium Levels
Find your care
We deliver effective, minimally invasive treatments in a caring environment. Call to connect with an expert in endocrine surgery.
Normal Blood Calcium Levels in Humans
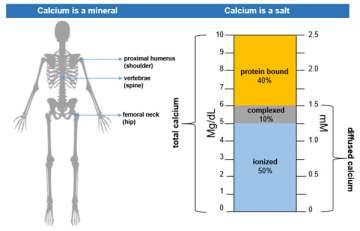
In our bodies, calcium is a mineral that makes up our bones, as well as a salt that dissolves in our blood and regulates bodily function. At UCLA, the normal blood calcium level is a range of 8.6 to 10.3 mg/dL.
In order to maintain a normal calcium level, the body uses hormones to regulate blood calcium levels.
The normal regulation of calcium in our blood stream is similar to the way a thermostat works. The body is set to have a normal amount of calcium (somewhere between 8.6 to 10.3 mg/dL).
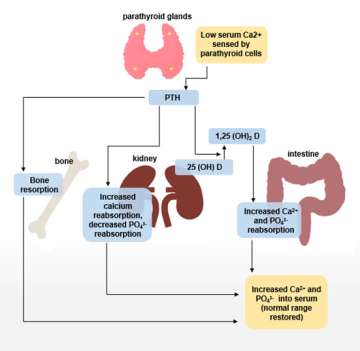
The parathyroid glands can be thought of as the “calcium thermostat” of the body.
The parathyroid glands are a group of four glands neighboring the thyroid gland that are the main regulators of the blood calcium levels in your body (see Parathyroid Glands-Illustration).

Parathyroid glands release parathyroid hormone (PTH), which increases your blood calcium levels. If the calcium levels are too low, the parathyroid glands will release PTH that will raise blood calcium to the appropriate levels. If the calcium levels are too high, the parathyroid glands will stop releasing PTH to try to bring the calcium back down to normal.
| Lab | Normal range (conventional units) | Normal Range (SI units) |
|---|---|---|
| Calcium (serum) | 8.6-10.3 mg/dL | 2.2-2.6 mmol/L |
| Calcium (ionized) | 4.4-5.2 mg/dL | 1.1-1.3 mmol/L |
| PTH (parathyroid hormone) | 11-51 pg/mL | 11-51 ng/L |
| Creatinine (marker of kidney function) | 0.6-1.3 mg/dL | 53.0-114.9 µmol/L |
| Vitamin D 25,hydroxy | 30-80 ng/mL | 121.4-323.7 nmol/L |
What Is a High Calcium Level?
Your blood calcium level would be considered high if it surpasses the upper limit of the normal range, meaning it is greater than 10.3 mg/dl. Keep in mind that “normal” reference ranges may differ depending on who is processing your labs. This is because different laboratories use varying groups of people who are considered ‘normal’ to determine reference ranges. It is important to re-check your calcium levels after receiving one elevated blood calcium result to confirm high calcium levels, otherwise called hypercalcemia. See Hypercalcemia.
Workup for High Calcium
After confirming a high calcium, your physician would then typically run a parathyroid hormone laboratory panel. The results of this panel will reveal whether or not your high calcium level is due to over-production of PTH from the parathyroid glands (see High Calcium).
Uncommonly, high blood calcium levels are due to something other than hyperparathyroidism, such as cancers or malignancies not from the parathyroid gland. However, in most patients, high calcium levels are caused by hyperparathyroidism, a condition when the parathyroid glands produce too much parathyroid hormone.
High levels of parathyroid hormone lead to the movement of calcium from the bone and into the blood. Thus, hyperparathyroidism can lead to weaker bones, bone fractures, and other complications such as kidney stones. See Hyperparathyroidism.
Other Common Calcium Lab Ranges
| Age | Males (mg/dL) | Females (mg/dL) |
|---|---|---|
| LabCorp Normal Calcium Reference Ranges | ||
| 18-59 years | 8.7-10.2 | 8.7-10.2 |
| >59 years | 8.6-10.2 | 8.7-10.3 |
| Quest Labs Normal Calcium Reference Ranges | ||
| 20-49 years | 8.6-10.3 | 8.6-10.2 |
| >49 years | 8.6-10.3 | 8.6-10.4 |
Have Questions About Normal and High Calcium Levels?