IVC Filter Placement
Find your care
Our clinic is nationally and internationally renowned for IVC filter removal. Call to learn more about the IVC Filter Clinic at UCLA Health.
Treatment for:
DVT (deep vein thrombosis) and/or PE (pulmonary embolism)
Why it’s done:
DVT and PE are typically treated with anticoagulation (blood thinners). If blood thinners cannot be used, or are not effective, then a filter may be placed in the large vein which drains blood from the legs (the IVC, or inferior vena cava). The filter traps clots coming up from the legs, preventing potentially deadly clot passage into the lungs (PE).
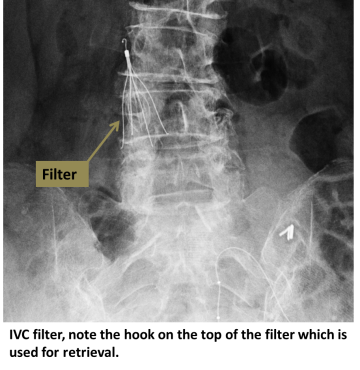
How it’s done:
An interventional radiologist uses ultrasound to access the jugular vein at the neck, or the femoral vein at the groin. Contrast dye is injected to determine size and anatomy of the IVC. The filter is then deployed at the appropriate position in the IVC, where small hooks affix it to the wall.
Level of anesthesia:
Conscious sedation
Risks:
Bleeding, infection, migration of the filter and fracture of the filter can rarely occur. Clot can form in the filter or below the filter, sometimes enough to completely occlude the IVC or the veins below the IVC.
Post-procedure:
Two to four hours of bed rest to prevent bleeding at the access site.
Follow-up:
Most IVC filters are retrievable. Once the filter is no longer needed, contact your interventional radiologist to arrange removal of the filter.