Normal Thyroid Hormone Levels
Find your care
We deliver effective, minimally invasive treatments in a caring environment. Call to connect with an expert in endocrine surgery.
What are Normal Thyroid Hormone Levels?
What is thyroid hormone?
Thyroid hormone is made by the thyroid gland, a butterfly-shaped endocrine gland normally located in the lower front of the neck. Thyroid hormone is released into the blood where it is carried to all the tissues in the body. It helps the body use energy, stay warm and keeps the brain, heart, muscles, and other organs working as they should.
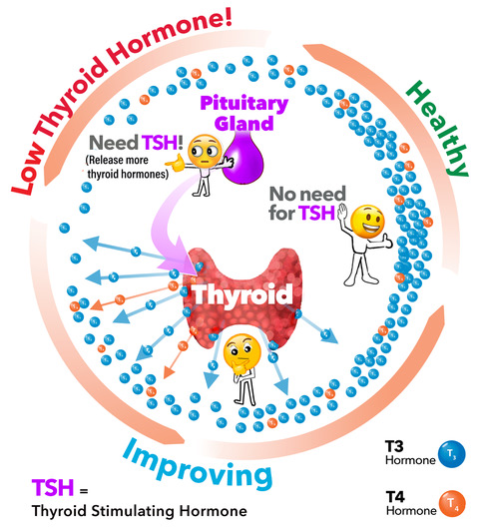
What Does the Thyroid Gland Do?
The thyroid is a small butterfly-shaped gland that sits in front of the trachea or windpipe. It is responsible for producing thyroid hormone (T4 and T3), which is involved in regulation of metabolism, bowel function, heart rate, temperature sense, menstrual regularity, and other functions.

The thyroid is controlled by the pituitary gland in the brain. The pituitary gland produces Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH), which controls the secretion of hormone from the thyroid gland.
Thyroid hormone exists in two main forms: thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). T4 is the primary form of thyroid hormone circulating in the blood (about 95%). To exert its effects, T4 is converted to T3 by the removal of an iodine atom; this occurs mainly in the liver and in certain tissues where T3 acts, such as in the brain. T3 normally accounts for about 5% of thyroid hormone circulating in the blood.
Most thyroid hormone in the blood is bound by protein, while only a small fraction is "free" to enter tissues and have a biologic effect. Thyroid tests may measure total (protein bound and free) or free hormone levels.
Production of thyroid hormone by the thyroid gland is controlled by the pituitary, another endocrine gland in the brain. The pituitary releases Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (abbreviated TSH) into the blood to stimulate the thyroid to make more thyroid hormone. The amount of TSH that the pituitary sends into the bloodstream depends on the amount of thyroid hormone in the body. Like a thermostat, if the pituitary senses low thyroid hormone, then it produces more TSH to tell the thyroid gland to produce more. Once the T4 in the bloodstream goes above a certain level, the pituitary’s production of TSH is shut off. In this way, the pituitary senses and controls thyroid gland production of thyroid hormone. Endocrinologists use a combination of thyroid hormone and TSH testing to understand thyroid hormone levels in the body.
What is a TSH test?
Thyroid tests
Blood tests to measure low or high TSH levels are readily available and widely used. Not all thyroid tests are useful in all situations.
TSH Test
The best way to initially test thyroid function is to measure the TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone) level in a blood sample. Changes in TSH can serve as an "early warning system" — often occurring before the actual level of thyroid hormones in the body becomes too high or too low.
A high TSH level indicates that the thyroid gland is not making enough thyroid hormone (primary hypothyroidism). On the other hand, a low TSH level usually indicates that the thyroid is producing too much thyroid hormone (hyperthyroidism). Occasionally, a low TSH may result from an abnormality in the pituitary gland, which prevents it from making enough TSH to stimulate the thyroid (central hypothyroidism). In most healthy individuals, a normal TSH value means that the thyroid is functioning properly.
What is a T4 test?
T4 Tests
A Total T4 test measures the bound and free thyroxine (T4) hormone in the blood. A Free T4 measures what is not bound and able to freely enter and affect the body tissues.
What does it mean if T4 levels are abnormal?
Importantly, Total T4 levels are affected by medications and medical conditions that change thyroid hormone binding proteins. Estrogen, oral contraceptive pills, pregnancy, liver disease, and hepatitis C virus infection are common causes of increased thyroid hormone binding proteins and will result in a high Total T4. Testosterone or androgens and anabolic steroids are common causes of decreased thyroid hormone binding proteins and will result in a low Total T4.
In some circumstances, like pregnancy, a person may have normal thyroid function but Total T4 levels outside of the normal reference range. Tests measuring free T4 – either a free T4 (FT4) or free T4 index (FTI) – may more accurately reflect how the thyroid gland is functioning in these circumstances. An endocrinologist can determine when thyroid disease is present in the context of abnormal thyroid binding proteins.
What is a T3 test?
T3 Tests
T3 tests measure triiodothyronine (T3) levels in the blood. A Total T3 test measures the bound and free fractions of triiodothyronine. Hyperthyroid patients typically have an elevated Total T3 level. T3 tests can be used to support a diagnosis of hyperthyroidism and can determine the severity.
In some thyroid diseases, the proportions of T3 and T4 in the blood change and can provide diagnostic information. A pattern of increased T3 vs T4 is characteristic of Graves’ disease. On the other hand, medications like steroids and amiodarone, and severe illness can decrease the amount of thyroid hormone the body converts from T4 to T3 (active form) resulting in a lower proportion of T3.
T3 levels fall late during hypothyroidism and therefore are not routinely used to evaluate patients with underactive or surgically absent thyroid glands.
Measurement of Free T3 is possible but is often not reliable and therefore may not be helpful.
What is a normal thyroid (hormone) level?
To assess thyroid hormone status for low or high TSH levels we use TSH and FT4 tests. The normal value for a laboratory test is determined by measuring the hormone in a large population of healthy individuals and finding the normal reference range. Normal ranges for thyroid tests may vary slightly among different laboratories, and typical ranges for common tests are given below.
TSH normal values are 0.5 to 5.0 mIU/L. Pregnancy, a history of thyroid cancer, history of pituitary gland disease, and older age are some situations when TSH is optimally maintained in a different range as guided by an endocrinologist.
FT4 normal values are 0.7 to 1.9ng/dL. Individuals taking medications that modify thyroid hormone metabolism and those with a history of thyroid cancer or pituitary disease may be optimally managed with a different normal FT4 range.
Total T4 and Total T3 levels measure bound and free thyroid hormone in the blood. These levels are influenced by many factors that affect protein levels in the body, including medications, sex hormones, and liver disease.
A normal Total T4 level in adults ranges from 5.0 to 12.0μg/dL.
A normal Total T3 level in adults ranges from 80-220 ng/dL.
Free T3 assays are often unreliable and not routinely used to assess thyroid function.
What does it mean if my thyroid levels are abnormal?
| Lab results | Consider... |
|---|---|
| High TSH, low thyroid hormone level | Primary hypothyroidism |
| High TSH, normal thyroid hormone level | Subclinical hypothyroidism |
| Low TSH, high thyroid hormone level | Primary hyperthyroidism |
| Low TSH, normal thyroid hormone level | Early or mild hyperthyroidism |
| Low TSH, high thyroid hormone level Followed by… High TSH, low thyroid hormone level | Thyroiditis (Thyroid Inflammation) |
| Low TSH, low thyroid hormone level | Pituitary disease |
Patterns of thyroid tests associated with thyroid disease
Primary Hypothyroidism
A high TSH and low thyroid hormone level (e.g. low FT4) can indicate primary hypothyroidism. Primary hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland makes too little thyroid hormone. Symptoms of hypothyroidism can include feeling cold, constipation, weight gain, slowed thinking, and decreased energy.
Causes of primary hypothyroidism include:
- Autoimmune thyroid disease, including Hashimoto's thyroiditis
- Thyroid gland dysfunction due to a medication (e.g. amiodarone, tyrosine kinase inhibitors, or cancer immunotherapy)
- Removal of all or part of the thyroid gland
- Radiation injury to the thyroid (e.g. external beam radiation, radioactive iodine ablation treatment)
- Excess treatment with anti-thyroid medications (e.g. methimazole, propylthiouracil)
Early or mild hypothyroidism may present as a persistently high TSH and a normal FT4 hormone level. This pattern is called subclinical hypothyroidism and your doctor may recommend treatment. Over time, untreated subclinical hypothyroidism can contribute to heart disease.
It is important to remember that normal TSH levels in older individuals (ages 70 and above) are higher than the normal ranges for younger individuals.
Primary Hyperthyroidism
A low TSH and a high thyroid hormone level (e.g. high FT4) can indicate primary hyperthyroidism. Primary hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland makes or releases too much thyroid hormone. Symptoms of hyperthyroidism can include tremors, palpitations, restlessness, feeling too warm, frequent bowel movements, disrupted sleep, and unintentional weight loss.
Causes of primary hyperthyroidism include:
- Graves' disease
- Toxic or autonomously functioning thyroid nodule
- Multinodular goiter
- Thyroid inflammation (called thyroiditis) early in the course of disease
- Thyroid gland dysfunction due to a medication (e.g. amiodarone or cancer immunotherapy)
- Excess thyroid hormone therapy
Early or mild hyperthyroidism may present as a persistently low TSH and a normal FT4 hormone level. This pattern is called subclinical hyperthyroidism and your doctor may recommend treatment. Over time, untreated subclinical hyperthyroidism can worsen osteoporosis and contribute to abnormal heart rhythms.
Thyroiditis
Thyroid inflammation, also called thyroiditis, causes injury to the thyroid gland and release of thyroid hormone. Individuals with thyroiditis usually have a brief period of hyperthyroidism (low TSH and high FT4 or Total T4) followed by development of hypothyroidism (high TSH and low FT4 or Total T4) or resolution.
Some forms of thyroiditis are transient, like post-partum thyroiditis or thyroiditis following an infection, and often resolve on their own without need for medication.
Other forms of thyroiditis, like thyroiditis resulting from cancer immunotherapy, interferon alpha, or tyrosine kinase inhibitors, usually result in permanent hypothyroidism and require long term treatment with thyroid hormone replacement.
Your endocrinologist will monitor your thyroid tests during thyroiditis and can help determine if you need short- and long-term medications to balance your thyroid function and control any symptoms.
Central Hypothyroidism
A low TSH and a low FT4 may indicate pituitary disease. Detection of central hypothyroidism should prompt your doctor to check for problems in other pituitary hormones, an underlying cause, and you may need imaging tests to look at the pituitary gland.
Central hypothyroidism is treated with thyroid hormone replacement. Importantly, adequacy of thyroid replacement in central hyperthyroidism is assessed with FT4 and Total T4 tests not TSH as in primary hyperthyroidism, and deficiency in stress hormone cortisol should be assessed before starting thyroid treatment to prevent an adrenal crisis.
Causes of central hypothyroidism include pituitary gland disease, such as a pituitary mass or tumor, history of pituitary surgery or radiation, pituitary inflammation (called hypophysitis) resulting from autoimmune disease or cancer immunotherapy, and infiltrative diseases.
Rare causes of abnormal thyroid function
Thyroid hormone resistance
Iodine induced hyperthyroidism
TSH-secreting tumor (TSH-oma)
Germ cell tumors
Trophoblastic disease
Infiltrative diseases, such as systemic scleroderma, hemochromatosis, or amyloidosis.
When abnormal thyroid function tests are not due to thyroid disease
While blood tests to measure thyroid hormones and thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) are widely available, it is important to remember that not all tests are useful in all circumstances and many factors including medications, supplements, and non-thyroid medical conditions can affect thyroid test results. An endocrinologist can help you make sense of thyroid test results when there is a discrepancy between your results and how you feel. A good first step is often to repeat the test and ensure there are no medications that might interfere with the test results. Below are some common reasons for mismatch between thyroid tests and thyroid disease.
Non-thyroidal illness
Significant illness, such as an infection, cancer, heart failure, or kidney disease, or recent recovery from an illness can cause transient changes in the TSH. Fasting or starvation can also cause a low TSH. An endocrinologist can help to interpret changes in thyroid function tests in these circumstances to distinguish non-thyroid illness from true thyroid dysfunction.
Test interference
Biotin, a common supplement for hair and nail growth, interferes with many thyroid function tests and can lead to inaccurate results. Endocrinologists recommend stopping biotin supplements for 3 days before having a blood test for thyroid function.
Individuals who have exposure to mice, like laboratory researchers and veterinarians, may develop antibodies against mouse proteins in their blood. These antibodies cross react with reagents in multiple thyroid function tests and cause unpredictable results. A specialized assay can accurately measure thyroid hormone levels and TSH in this circumstance.
I don't feel well, but my thyroid tests are normal
Thyroid blood tests are generally accurate and reliable. If you do not have low or high TSH levels and your thyroid tests are normal, your symptoms may not be related to thyroid disease, and you may want to seek additional evaluation with your primary care physician.
How is hypothyroidism treated?
What is thyroid medication?
Thyroid Hormone Treatment
Levothyroxine is the standard of care in thyroid hormone replacement therapy and treatment of hypothyroidism. Levothyroxine (also called LT4) is equivalent to the T4 form of naturally occurring thyroid hormone and is available in generic and brand name forms.
How do I take levothyroxine?
To optimize absorption of your thyroid medication, it should be taken with water at a regular time each day. Multiple medications and supplements decrease absorption of thyroid hormone and should be taken 3–4 hours apart, including calcium and iron supplements, proton pump inhibitors, soy, and multivitamins with minerals. Because of the way levothyroxine is metabolized by the body, your doctor may ask you to take an extra pill or skip a pill on some days of the week. This helps us to fine tune your medication dose for your body and should be guided by an endocrinologist.
For patients with celiac disease (autoimmune disease against gluten) or gluten sensitivity, a gluten free formulation of levothyroxine is available. Some individuals may have genetic variant that affects how the body converts T4 to T3 and these individuals may benefit from the addition of a small dose of triiodothyronine.
Liothyronine is replacement T3 (triiodothyronine) thyroid hormone. This medication has a short half-life and is taken twice per day or in combination with levothyroxine. Liothyronine alone is not used for treatment of hypothyroidism long term.
Other formulations of thyroid hormone replacement include natural or desiccated thyroid hormone extracts from animal sources. Natural or desiccated thyroid extract preparations have greater variability in the dose of thyroid hormone between batches and imbalanced ratios if T4 vs T3. Natural or animal sources of thyroid hormone typically contain 75% T4 and 25% T3, compared to the normal human balance of 95% T4 and 5% T3. Treatment with a correct balance of T4 and T3 is important to replicate normal thyroid function and prevent adverse effects of excess T3, including osteoporosis, heart problems, and mood and sleep disturbance. An endocrinologist can evaluate symptoms and thyroid tests to help balance thyroid hormone medications.
How do I know if my thyroid dose is correct?
Monitoring thyroid levels on medication
Correct dosing of thyroid hormone is usually assessed using the same tests for diagnosis of thyroid disease, including TSH and FT4. Thyroid tests are typically checked every 4-6 weeks initially and then every 6 to 12 months once stable. In special circumstances, such as pregnancy, a history of thyroid cancer, central hypothyroidism, amiodarone therapy, or use of combination T4 and T3 thyroid hormone replacement, your endocrinologist may check different thyroid tests. Additionally, your endocrinologist will evaluate for symptoms of hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism and perform a physical exam.
Women who are pregnant and women who may become pregnant should only be treated with levothyroxine (T4). Only T4 efficiently crosses the placenta to provide thyroid hormone to the developing fetus. Thyroid hormone is critical in early pregnancy for brain development. Normal ranges for thyroid tests in pregnancy are different and change by trimester. Women with thyroid disease in pregnancy or who are considering pregnancy should be under the care of an endocrinologist to guide therapy.
Individuals with a history of thyroid cancer, even if only a portion of the thyroid was removed, also have different target ranges for TSH and FT4 tests. Thyroid hormone replacement in these individuals is closely tied to ongoing thyroid cancer surveillance, monitoring of thyroid cancer tumor markers, and dynamic assessment of recurrence risk. These patients are optimally managed by a multidisciplinary team including an endocrinologist and endocrine surgeon.
Watch Thyroid Videos:
Graves’ Disease
Hyperthyroidism
Hypothyroidism
Thyroid Nodules
TSH and Thyroid Function Tests
Best Way to Take Thyroid Hormone...and more!
Have Questions About Normal Thyroid Hormone Levels? Please Contact Us.