Case: Phyllodes Tumors
by Sara Yang, MD and Nina Capiro, MD
Phyllodes tumors, also known as cystosarcoma phyllodes, represent a rare class of fibroepithelial tumors, accounting for only 0.3-1% of all breast neoplasms.2 Phyllodes tumors arise from periductal stroma and are characterized by increased stromal cellularity as well as epithelium lined clefts.1 Peak incidence is seen in middle-aged women between the ages of 30-40, although there are reported cases in women as young as 12 and as old as 87.3
Phyllodes tumors share many clinical, imaging and histological features with fibroadenomas. It is important, however, to differentiate the two tumors as phyllodes tumors demonstrate malignant potential. Phyllodes tumors are classified as benign, borderline, or malignant where imaging features cannot be reliably used for differentiation.3 Approximately 20-30% of phyllodes tumors are found to be malignant upon resection and up to 25% of malignant phyllodes tumors have been shown to metastasize.2
Clinically, phyllodes tumors often present as a rapidly growing painless lump. These tumors can often be very large in size. Often, the clinical context may be the only clue to help differentiate a phyllodes tumor from a fibroadenoma.
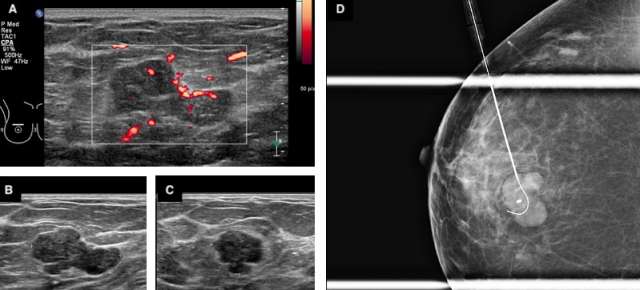
Certain imaging features that may help differentiate a phyllodes tumor from a fibroadenoma include size greater than 3 cm, irregular shape, microlobulated margins, complex heterogeneous echogenicity and internal hypervascularity.2,3 Phyllodes tumors may also be of higher density on mammography given their larger size at presentation.2 On MRI, phyllodes tumors are more likely to demonstrate heterogenous enhancement with internal cystic areas.2 When internal cystic areas are present, phyllodes tumors may demonstrate posterior acoustic enhancement on sonography.
As such, the recommended management for phyllodes tumors is surgical excision. Even when benign, phyllodes tumors carry up to a 25% chance of local recurrence after excision.1 Surgical excision with wide margins or even mastectomy for very large tumors may be necessary.

References
- Goel NB, Knight TE, Pandey S, Riddick-Young M, de Paredes ES, Trivedi A. "Fibrous Lesions of the Breast: Imaging-Pathologic Correlation." Radiographics. 2005 Nov-Dec;25(6):1547-59. . PMID: 16284134.
- Duman L, Gezer NS, Balcı P, Altay C, Başara I, Durak MG, Sevinç AI. "Differentiation between Phyllodes Tumors and Fibroadenomas Based on Mammographic Sonographic and MRI Features." Breast Care (Basel). 2016 Apr;11(2):123-7. . Epub 2016 Mar 23. PMID: 27239174; PMCID: PMC4881274.
- Clark, HR, Merchant, KA, Omar, LA, Compton, LM, Hayes, JC. "Breast Lesions in Women Aged Younger than 30 Years: Clinical Presentation, Diagnosis, and Management." Journal of Breast Imaging, 2020 January/February; 2(1), 72-80. .